CLICK HERE TO SUBMIT YOUR BODY PROFILE
Physical Training Principles:
CLICK HERE FOR BASIC WEIGHT TRAINING GUIDE
Reasons for Training
- Bodybuilding and Strength training
- Training for the sport of life
- Training for sports
- Training for Weight loss
- Body Shaping
- power lifting
Factors that determine training outcomes
· Chronological age- in years
· Biological age-body maturity
· Training age-how long you have been training
· Emotional maturity- your focus
· Gender
· Physical capability-combination of heredity and history
· Heredity-genetic muscle type (fast or slow twitch)
· Lifestyle- behavior in and out the gym
PHYSICAL TRAINING VOCABULARY (CLICK HERE)
How do muscles work?
- 3 types-cardiac(heart), smooth(organs), skeletal (attached to your bones)
- Training by overloading the muscle-destroying the muscles with training and allowing rapid repair and adaptation.
- Your body responses differently depending on your type of muscle domination- Slow twitch (fiber 1) which are made for long duration, low-intensity activity , slow to fatigue
- Fast twitch (fiber 2) – Produce powerful burst contract at high rates, don’t new oxygen to perform, can be further divided into 2a, 3b, and 2x fibers.
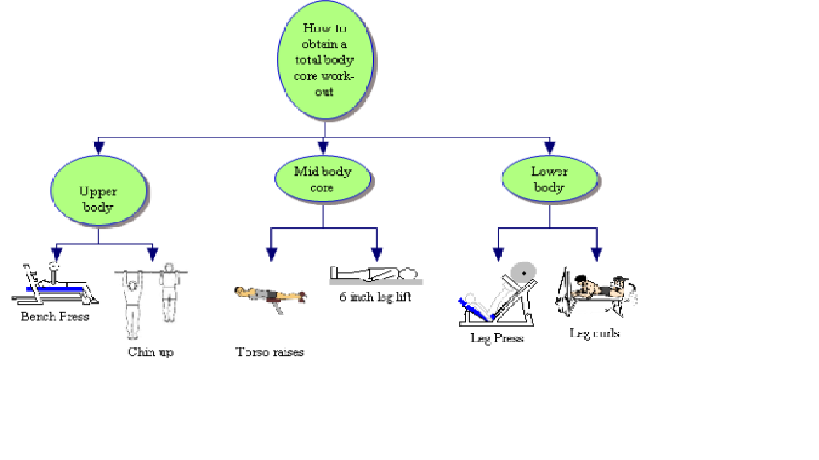
How to obtain a total body core work-out
I.
Upper body
A. Chin up
B. Bench Press
II. Lower body
A. Leg Press
B. Leg curls
III. Mid body core
A. 6 inch leg lift
B. Torso raises
Planning your Training
· Choose Specificity – If you want to training for Bulk, weight loss, Definition, etc.
· Overload- How intense is your workout (working out with 70%-80% of your 1 rep max). Working out per week or time frame is important to your level of your results.
· Progression- Increase your intensity each training cycle. It does not have to happen each training day in can be gradual.
· Recovery- Your rest time from working out is just as important as your training time. Your body needs time recover from the workouts to prevent over training.
Starting Off Training-Sets and Repetitions, don’t train the same muscles everyday,
1. Keep it Simple –Basic Simple Program
§ Chest and Triceps- Bench press
§ Back and Biceps-Pull-ups or bent over rows
§ Legs and lower back – Squat or deadlift
§ Shoulders-shoulder press
§ Biceps –standing biceps curl
§ Triceps- Dips
2. Rest more than training- In the beginning your body is not ready for the all out intense training. Be prepared for DOMS- Delayed Onset Muscles Soreness.
3. Alternative Style of training- Try doing Sets of repetitions which involves you training to failure.
4. Progress slowly- Everyone’s body does not respond the same. You will not be able to do large amounts of weight starting off.
5. Loading and Progression--- Put it all together--- For the first 6-8 weeks of training.
§ Select a weight for each exercise and allows your to perform 12-14 Reps before muscle failure but perform only 10 reps.
§ With each session, add around 3-5 lbs
§ Rest for around 3-5 minutes between sets, and try to complete 3 sets of each exercise. In these weeks you will enhance strength in the 12-14 repetition range. With this more manageable weights, focus on performing each exercise with a perfect technique to maximize adaptation.
6. For the Next 4-8 weeks
§ Continue to increase weight
§ Test your 1 rep max
§ Devote at least one session per week to training the lift to failure on each set.
§ Start using smaller progression weights (1 to 3 pounds increase between sets)
§ Take shorter rest periods between sets.
§ Use different training tools
Types of Routines
1. CIRCUIT TRAINING (1st semester)
2. SPLIT SET TRAINING (1st Semester)
3. DROP SETS (1st Semester)
4. PYRAMID TRAINING (1st Semester)
5. SUPER SET TRAINING (2nd Semester)
6. COMBINATION TRAINING (2nd Semester)
7. PLYOMETRICS (2nd Semester)
8. HIGH INTENSITY TRAINING H.I.T. (2nd Semester)